What is a Cell?
Cells are the basic structural,
functional, and biological units of all living beings. Cells are the smallest
units of life. A cell can replicate itself independently. Hence, cells are known
as the “building blocks of life”.
Each cell contains a fluid called the
cytoplasm, which is enclosed by a cell membrane. A cell is the smallest structural
and fundamental unit of life.
Chemical Composition of Cell
Cells are composed of water,
inorganic compounds, and carbon-containing (organic) compounds and elements.
Water is the most abundant constituent
in cells, it accounts for about 70% of total cell mass.
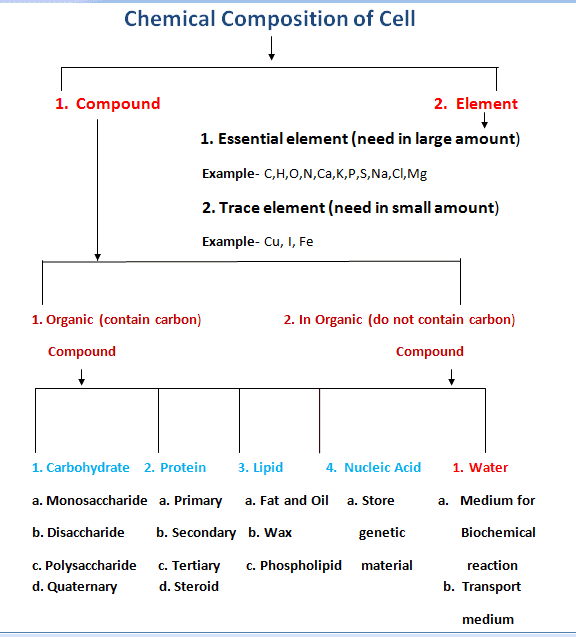
1. Carbohydrates
It is primary
source of energy.
2.
Proteins
a. To build
new cells for development and growth and renew damaged tissue or cells.
b. It required
for synthesis of enzymes, antibodies and hormones for various metabolic
activities.
c. It used to
form structural components
e. It aids in
synthesis of haemoglobin
f. Needed
for the cell repair, growth and maintenance.

1. Essential - Essential proteins are those which cannot be
synthesized by the body, get form dietary sources.
2. Non-Essential – Nonessential proteins synthesized or
produce by the body.
3. Lipids
a. It is a source of energy
b. It
involves in physical protection to major organs in the body.
c. Major
components of
plasma membrane
d. It is solvent (able to
dissolve) for fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K.
4. Nucleic Acid
Store
genetic information
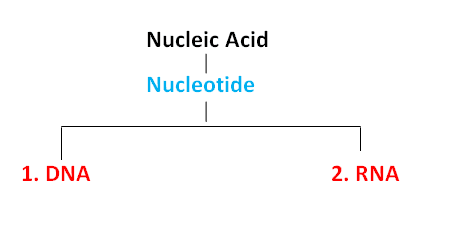
RNA and DNA are polymers (consisting of very large molecules, repeating subunits) made of long chains of nucleotides.
5. Water
a. It involves in biochemical reaction and transport medium
b. Maintaining osmotic balance and
turgidity
c. Maintain body temperature
d. Prevent from dehydration of cell
e. Act as lubrication
f. Work as solvent
Function of Elements in Animal cell
H, C, O, N -
Synthesis of organic compounds, for example - proteins, lipids, and
nucleic acid.
Na - Help in the transmission of nerve
impulse.
Mg - Involved in protein synthesis and acts
a cofactor.
Ca - Required formation of strong bone
and teeth, helps in contraction of muscle cells and promotes blood clotting.
Fe - Involve in synthesis of hemoglobin
and respiratory enzymes.
P - Formation of strong bone and teeth,
help in the contraction of muscle cell, synthesis of ATP and an essential component
of nucleic acid.
K - Required in muscle contraction and
transmission of nerve impulse..
Cl - Synthesis of
hydrochloric acid by the gastric gland in the stomach.







0 Comments