Intravenous Fluid - Types of IV Fluids and Their Uses
The intravenous (IV) is the
fastest way to deliver fluid replacement throughout the body as they are
introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed.
Intravenous fluid drip used to administer electrolytes
that contain selected vitamins and nutrients, that correct imbalance electrolyte administered directly into the vein; venous circulation.
Check out here what iv
cannulation sites for intravenous medication administration are.
IV Fluids Uses
IV Fluids is administered through intravenous (iv) route of
administration, commonly used for rehydration or to provide selected nutrition
for those who are unable to take food or water by mouth.
IV Fluids helps restore salt and electrolyte levels in the patient’s
body.
Know here what is the angle for
intravenous injection?
Types of Intravenous Fluids
Intravenous fluids are classified into two types-
1. Crystalloids solution
2. Colloids solution
1. Crystalloids Solution
Crystalloid is a solution in which crystals may form but are
able to diffuse across the cellular membrane.
Example of crystalloids solutions-
a. Normal saline
b. Ringer lactate
c. Dextrose5%
2. Colloids Solution
Colloids are glue-like substances, such as protein or starch, or a substance used as a plasma expander in place of blood.
Example of Colloids solution-
a. Dextran
b. Albumin
c. Hetastarch
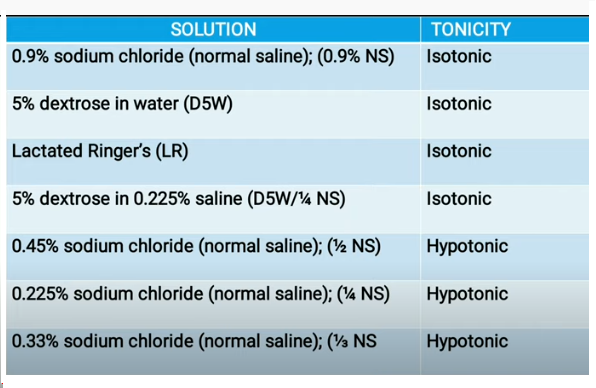
Types of Intravenous Solution
Intravenous solutions are three types-
1. Hypotonic solution
In hypotonic
solutions, water will move from the extracellular space into cells. This result, cell
to expand size and burst.
Example of hypotonic solution are; 0.45%
saline, 0.25% saline, 2.5% dextrose solution.
Hypotonic solutions are commonly used to give fluids
intravenously to hospitalized patients to treat or avoid dehydration.
2. Isotonic solution
In an isotonic solution, No movement of water between them. Same salt concentration as cells
and blood. this result, Cell neither swells nor
shrinks.
Examples of
isotonic solution are; 0.9% normal saline and lactated
ringers.
3. Hypertonic solution
In a hypertonic
solution, Movement of water from cells into extracellular space. A result,
Cell shrinks.
For example, hypertonic solutions are applied for
soaking wounds. It promotes healing in necrotic,
draining, or infected wounds.
Examples of hypertonic IV solutions are; 3% Normal Saline (3% NaCl), 5% Sodium Chloride, D5 in 0.9% normal saline, and D5 in lactated ringers.
Note - Osmolarity of Body; 285-295 mOsm/kg
Check out here types of iv
cannula and know the parts of iv
cannula.
How many Types of Fluids are given Intravenously?
Intravenous fluids are given through a drip into
the direct vein. It is administered to correct the electrolyte or acid-base
balance in the body.
These are -

1. NS- Normal saline water
NS 0.9%; 0.9g NaCl in each 100ml of NS.
Uses of Normal Saline water
a. Used in dehydration
b. Used for wound washing
c. Used to given injection
d. Used in an accident and in Diabetic patient
2. RL- Ringer Lactate Solution,
Hartmann’s Solution, Ringer Solution, Sodium Lactate Solution
Ringer lactate solution consists of-
1. Sodium lactate
2. NaCl - sodium chloride
3. Kcl - potassium chloride and
4. Cacl2 - calcium chloride present in RL
Uses of Ringer Lactate solution
a. Used in Diarrhea
b. Used in dehydration
c. Used in burn, accident
d. Used in dizziness, hypotension
3. DNS- Dextrose Sodium
Chloride Solution (D – Dextrose: Glucose)
5g Dextrose in each 100ml of NS.
Uses of DNS
a. Used in Dehydration
b. Used in Hypoglycemia
c. Used in insulin shock
Note - It is not used in Diabetic Patients.
Types of DNS solution
D5, D10, D25, D50, D5NS, D5LR
4. Mannitol Solution (Osmotic
Diuretic)
20 gm mannitol in 100ml of solution
Uses of Mannitol solution
a. Used in Diuretics
b. Used in Oligourea
c. Used in Oedema
d. Used in intraocular pressure









0 Comments