Introduction - Small Pox
Smallpox is an infectious ancient disease caused by the Variola
virus. Before smallpox was eradicated, it was a serious infectious and
contagious; disease; it spread from one person to another.
Epidemiological Triad
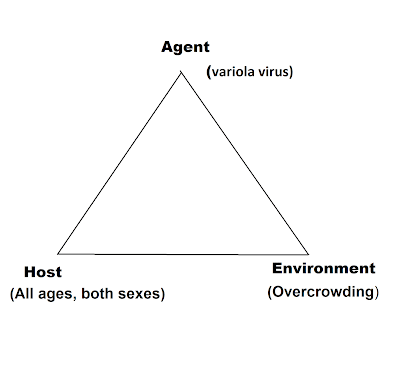
Agent - The causative agent of smallpox is the Variola virus (DNA virus).
Host - All age group, Both sexes
Environment - Overcrowded place
Mode of Transmission
Smallpox is an airborne disease. So this is the one of
reasons smallpox was so dangerous and deadly. Airborne diseases more tend to be
spread fast.
1. Droplet nuclei (aerosols formed)
2. Droplet infection (airborne
droplets)
3. Directly
from person to person – By coughing,
sneezing, or direct contact with any bodily fluids of an infected person.
4. Via
contaminated items - Sharing contaminated
material or object increase risk of infection such as clothing, bedding or
fomites.
Incubation Period
Infection with variola virus begins with an incubation
period usually between 7 to 17 days (range 10 to 14 days).
Clinical Manifestation
Sign and symptoms of smallpox include-
1. High fever as 101°F to 105°F
2. Chills
3. Headache
4. Severe backache
5. Abdominal pain
6. Vomiting
7. Convulsion
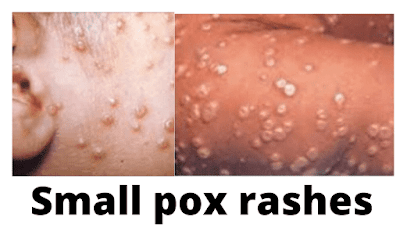
8. Appearance of rashes in centrifugal distribution
9. Severe fatigue
Early symptoms include high fever headache, and a backache.
Then the virus produces a characteristic rash, the rash
started on the face and then spread to the hands, forearms, and the main part
of the body.
How smallpox spread?
Variola virus spread through coughed or sneezed and droplets
from nose or mouth of infected person to to other people.
The variola virus can also spread through contaminated
materials or object such as bedding or clothing of infected person.
A small red spots (early rash stage) starts as on the tongue and in the mouth. These spots are developed
into sores and that breaking open, large amounts of the virus spread into the
mouth and throat. The person continues experience to have a fever.
When sores in the mouth start breaking a rash developed on
the skin, appears on the face and start spreading to the arms and legs, and
then also to the hands and feet.
The rash developed into spots become filled with clear fluid
and then turn into abscesses filled with
fluid and pus. Later these abscesses break open, form a crust and scab dries up
and falls off and leaving mark scars.
Scabs and the fluid found in the sores of smallpox patient’s
also contained the variola virus.
Types of Smallpox
There were two common forms of smallpox were known as variola
minor, which causes mild smallpox, and variola
major, which severe form of smallpox, with a more extensive rash and higher
fever. It is most common form of smallpox.
Treatment for Smallpox
For smallpox, there is no cure. As a result of worldwide,
repeated vaccination programs had executed. Officially declared that variola
virus (smallpox) has been completely eradicated.
Complications of Smallpox
Most people who infected with smallpox get survive. These
infection cause severe forms in pregnant women and people with weakened immune
systems.
Those people recovered from smallpox mostly have severe
lifelong scars, especially on their face, arms and legs and in some person
smallpox cause blindness.
Prevention of Smallpox
1. Isolate the infected person to control the spread
of the virus
2. Smallpox vaccination
Smallpox
infection can be preventable by smallpox vaccine, called vaccinia virus
vaccine. The smallpox vaccine is made from a vaccinia which is a
poxvirus.
Currently, the vaccine for smallpox is not available for general
public because smallpox had eradicated, and virus no longer exists in nature.
Smallpox FAQ
1. What is smallpox?
Smallpox is an infectious ancient
disease. Causative agent of smallpox is Variola virus.
2. How does smallpox spread?
Variola virus transmitted through coughed or sneezed and
droplets from infected person to other or spread through sharing contaminated
materials or objects such as bedding or clothing of infected person.
3. Is a smallpox vaccine currently
available?
Vaccine against smallpox infection
was a key tool for was eradication of smallpox. it protected humans against
smallpox disease. Since small pox disease eradicated, vaccine is not
recommended in routine immunization for general public.
Vaccine can be used to protect anyone
who has a high risk of exposure to smallpox.
4. Can smallpox be treated?
There is no cure for smallpox
infection, but vaccination can be used very effectively to prevent infection
from developing infection.
since smallpox was eradicated, New antiviral drugs available, for treatment of smallpox infection.
5. What is the difference between smallpox and chickenpox?
The causative agent of Smallpox is Variola virus (Pox Virus) and the causative agent of Chickenpox is Varicella Zoster Virus (Herpes Virus).








0 Comments