Vital Signs - Measure Respiration Rate/ Breathing Rate
Respiration is the act of breathing that includes the intake of
oxygen (O2) and the removal of carbon dioxide (CO2).
Respiration rate is the number of breaths taken per
minute. Measuring respiration rate is a primary vital sign. Vital
sign includes; TPR and blood
pressure.
What is the Respiratory rate?
Respiration rate indicates the number of times the person
breaths in and out in one minute. It refers to the number of breaths a person takes
per minute.
It observes by a
complete respiration cycle; Inspiration + Expiration.
Normal Respiratory rate/ Breathing rate
The normal respiratory rate or breathing rate for adults is
16 to 22 breaths per minute.
Check
out here normal
temperatures for adults.
What is Ventilation?
The exchange of air between the lungs and the
atmosphere/environment via inhalation and exhalation so that oxygen can be
exchanged for carbon dioxide in the alveoli (tiny air sacs in the lungs).
Know here what is normal
pulse rate by age?
Normal Value of Respiration rate by Age
Respiratory rate normal ranges-
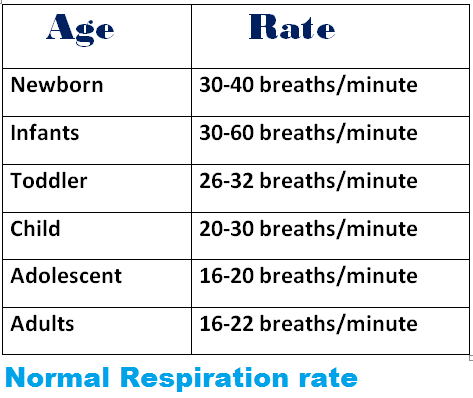
Know here, blood pressure range in adults.
Purpose of Observe Respiration rate
1. To determine baseline respiratory rate for comparisons.
2. Observe the respiratory pattern of clients.
3. To monitor change in oxygenation or in respiration.
4. To evaluate the patient's response to medication or
treatments that affects the respiratory system.
Respiration Pattern Characteristics
1. Respiration rate
It indicates the number of times the person breaths in and
out in one minute.
2. Depth
It is observed by the movement of the chest during
inspiration, which may be deep or shallow.
a. Deep; a large volume of air inhaled and exhaled.
b. Shallow;
too slow, Exchange of a small volume of air minimal use of lung tissue.
3. Rhythm
It is observed by a regular repeated pattern of respiration and
It indicates the equal interval between two respirations.
Method of Observe Breathing rate

1. Costal (Thoracic movement)
Observed by the movement of chest
upward and downward for a complete minute. This method is commonly used for adults
for counting their respiratory rate.
2. Diaphragmatic (Abdominal movement)
Involves the contraction and relaxation
of the diaphragm, observed by the movement of the abdomen. This method is commonly
used for children for counting their respiratory rate.
.
1. Bradypnea
A decreased respiratory rate is less than
10 breaths/min.
2. Tachypnea
An increased respiratory rate is more than 24 breaths/min
3. Hypoxia
Hypoxia is a state in which the supply
of oxygen in tissue is insufficient for normal life functions.
4. Hypoxemia
Hypoxemia is low oxygen in your blood that can cause hypoxia (low oxygen in your tissues) when your blood doesn't carry
enough oxygen to your tissues to meet your body's needs.
5. Anoxia
Anoxia is an extreme form of hypoxia, in
which there is a complete loss of oxygen supply to the body.
6. Hyperoxia
Hyperoxia is a state of excess supply
of O2 in tissues and organs.
7. Hypocarbia/Hypocapnia
The state of having abnormally reduced
levels of carbon dioxide in the blood. The result from hyperventilation.
8. Hypercarbia/Hypercapnia
Hypercarbia is when you have too much
carbon dioxide (CO2) in your bloodstream. Result of hypoventilation.
9. Eupnea
Normal breathing
9. Apnea
Apnea is the
cessation(stop) of breathing, in which no movement of the muscles of
inhalation.
10. Hypopnea
Hypopnea is typically defined by a
Lower amount of air movement into the lungs and can cause a drop in oxygen levels in
the blood.
11. Hyperapnoea (forced respiration)
An increase in the depth of respiration,
It is characterized by deep breathing.
12. Hypoventilation
A condition in which a reduced amount of air enters the alveoli in the lungs, resulting in decreased levels of oxygen and increased levels of carbon dioxide in the blood. It causes too slow breathing.
13. Hyperventilation
A state in which breathing is deeper
and more rapid than normal. It can lower carbon dioxide in the blood.
14. Dyspnea/Dyspnoea
Difficult or labored breathing, shortness of breath.







0 Comments