Types of Cell Division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more cells called daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs a part of the larger cell cycle.

What is the Cell Cycle?
Cell cycle is the period from the beginning of one cell
division to the beginning of next cell division.
The cell cycle has two major phases; the interphase (G₁, S, and G₂ phases), followed by the
mitotic phase (mitosis and cytokinesis), and the G₀ phase.
The different stages of mitosis and cytokinesis altogether
define the Mitotic or M phase of an animal cell cycle.
A. Interphase
B. Cell division
A. Interphase
Interphase has three major phases -
1. G1 gap phase: first gap phase (Growth phase)
2. S Phase (Synthesis)
3. G2 Phase (Second gap phase)
B. Cell Division
There are two steps in cell division-
1. Nuclear division (mitosis and meiosis)
2. Cytoplasmic division or cytokinesis
Types of Cell Division
1. Somatic Cell
Division
Somatic
cells in non-reproductive cells. Somatic
cell division takes place in somatic cells (body cells except for gametes), for growth,
development, and repair.
Somatic cell division includes; Mitosis and Cytokinesis.
Phases of Mitosis
Mitosis phases are –
1. Prophase (pro-before)
a. Early prophase
b. Late prophase
2. Prometaphase
3. Metaphase
4. Anaphase
a. Early Anaphase
b. Late Anaphase
5. Telophase
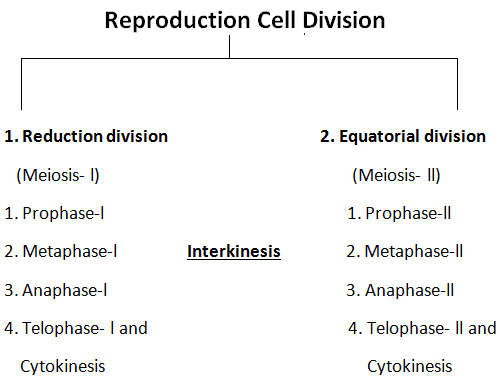
2. Reproduction Cell Division
Reproduction cell division includes; Meiosis and Cytokinesis.
Check out here stages of meiosis; meiosis-l, meiosis-ll.
Cell Cycle - Phase of Cell Cycle
1. Interphase
Cell spends
most of its time in interphase to grow,
replicate chromosomes and prepare for cell division. Then cell leaves
interphase, undergoes mitosis or meiosis division.
During interphase occurs-
1. Cell growth
2. DNA in the nucleus replicates
3. Great metabolic activity
4. Occupying about 90% of total duration (time) of cell
cycle
5. Activity of like cell growth, cellular respiration and
RNA and protein synthesis takes place.
6. It sets stages for cell division.
An interphase portion has a three-stage -
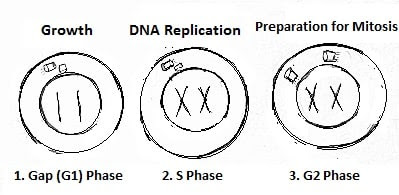
a. G1-gap phase - “first gap”
1. Cell are engaged in growth, metabolic activity and
production of substances require for cell division.
2. Cell grows in size and synthesizes mRNA and protein
which is required for DNA synthesis.
3. Preparation for DNA synthesis and DNA replication (copies
DNA).
4. Cell duplication organelles and cytosolic component are
increases.
5. For a cell with a total cell cycle time of 24 hours, G1
lasts for 8 to 11 hours.
b. S phase (synthesis)
1. Known as S phase because DNA is synthesized
2. DNA is replicated
3. Genetic material is doubled, chromosome duplicate itself
4. Centrioles duplicate in S phase.
5. S phase is controlled by n enzyme called
cdc2kinase.
6. The phase lasts for 6to 8 hours.
3. G2 Phase – second gap phase
1. Rapid cell growth
2. Prompt protein synthesis and cell prepare itself for
mitosis.
3. Centriole pair start to move apart to prepare next cell
division.
4. The cell “double-check” the duplicated chromosomes for
error, making repair if any needed.
5. Leads to mitosis phase, this phase lasts 4 to 6 hours.
4. G0 Phase
Known as resting phase. In which those cells don’t divide, these resting cells exit
the cell cycle and enter the G0 phase.
Get here details on cell Cycle or cell Division Cycle.









0 Comments