What is Mitosis?
Mitosis occurs only in
eukaryotes cells.
In prokaryotic cells
that lack a nucleus, divide by
a different process called binary fission. Prokaryotes aren't undergone mitosis or meiosis.
Mitosis is a part of
the cell cycle in which one cell divides into two genetically identical
daughter cells. in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei and then divide by cytokinesis (cytoplasmic division) to produce
genetically identical two daughter cells.
Mitosis is also known
as equational division.
Check out what
is cell
division and cell cycle?
Types of Cell Division
These
types are-
1. Somatic Cell
Division
a.
Mitosis (equational division)
b.
Cytokinesis (cytoplasmic division)
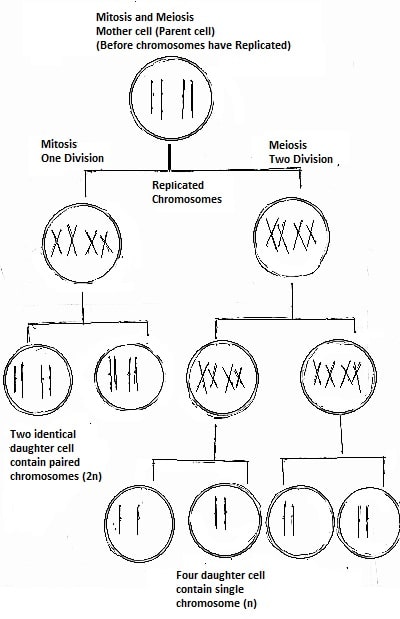
Mitosis
produces two diploids (2n) cells.
2. Reproduction Cell Division
a.
Meiosis (Meiosis-l Meiosis-ll)
b.
Cytokinesis
Meiosis
produces 4 haploid (n) cells.
Mitosis - Somatic Cell
Division
After completing the
G1Phase, S Phase, G2Phase called interphase, cells enter into mitosis for
cell division.
In mitosis, division
mother cell into two diploid daughter cells genetically identical to each
other.
Phases of Mitosis
Mitosis is involved
five stages-
1. Prophase
a.
Early Prophase
b.
Late Prophase
2.
Prometaphase
3. Metaphase
4.
Anaphase
a.
Early anaphase
b. Late anaphase
5. Telophase

1. Prophase- Mitosis begins at prophase
a. Early
prophase
1. Chromatin thread
begins to coil, they shorten, coil, thicken.
2. Nucleoli and
nuclear envelope begin to break up.
3. Mitotic spindle
start to form
4. Prepare the
stage for the division of the chromosomes.
b. Late
prophase
1. Nucleoli disappear
2. Nuclear
envelop (nuclear membrane) breakdown and is absorbed in the cytosol.
3. Centrosome and
their centrioles each migrate to opposite poles of the cell.
5. Centrosomes are
move to opposite poles of the cell then the mitotic spindle then forms between
the two centrosomes.
4. Mitotic spindle
grows and begins to capture and organize the chromosome.
2. Prometaphase
In prometaphase,
kinetochores (protein complex) appear at the centromeres and mitotic spindle
microtubules attach to kinetochores.
3. Metaphase
1. Microtubules of the
spindle have attached to kinetochores (protein complex develops around the
centromere, providing attachments between the chromosomes and microtubules
of the spindle).
2. Chromosome lined up
on the midpoint region (metaphase plate). Chromosomes become aligned at the spindle equator, to form a
metaphase plate.
3. End of metaphase
centromere doubled. So that each chromatid has its own centromere.
4. Sister chromatids
are pulled, move toward opposite spindle poles of the cell.
4. Anaphase
The anaphase stage
Involves early and late anaphase.
During early
anaphase or Anaphase A
1. Sister chromatids
are separate
2. Splitting and
separation of centromeres.
3. Movements of two
sister chromatids of each pair toward opposite poles of the cell.
During early
anaphase or Anaphase B
1. Separation of the
sister centrosomes to their opposite poles and remain attached to the spindle
fibers by their centromeres.
2. Cytokinesis may
begin in which cleavage furrow is induced by the mitotic spindle during late
anaphase.
5. Telophase
1. Chromatids reach
opposite pole
2. Chromosomes begin
to uncoil (rod-like form)
3. Spindle is dissolve
4. New nuclear envelope
is formed
7. Cytokinesis occurs
in which cells split into two identical daughter cells.
Cytokinesis
1. Mitosis is followed
by cytokinesis.
2. Separation of
cytoplasm into two parts.
3. Separation is done
by cleavage “furrow- a pinching” of the plasma membrane.
4. Cells splits into
two, which result produces two separated genetically identical daughter cells.
5. Cytokinesis may
start during late anaphase or telophase.
Know here what
meiosis cell division is and what phases of
meiosis are.









0 Comments