Endoplasmic Reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is a network of membrane-enclosed flattened sacs is made up of tubules, cisterns or cisternae, and
vesicles that connected to the nuclear envelope and extend within the
cytoplasm.
Endo- Inside
Plasmic - Cytoplasm
Reticulum - Network
The surface of ER may or may not associate with ribosomes. ER
is actively involved in the synthesis of proteins, protein folding,
processing, modification, and transport.
ER also participates in lipid and steroid synthesis,
carbohydrate metabolism, and calcium storage to the site of storage or
utilization.
Read here function of ribosome
and function
of golgi apparatus.
Structure of Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
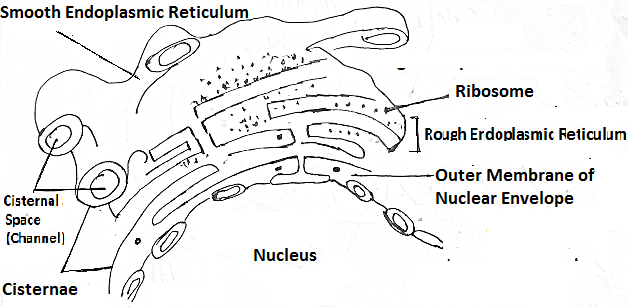
Depending upon the Presence or Absence of ribosomes, ER is
two types -
1. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
2. Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
1. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
SER has a smooth membrane and doesn't bear ribosomes
mean a lack of ribosome. It is a site of fatty acid, phospholipid, and steroid
synthesis.
SER is largely associated with lipid (fat) synthesis and
metabolism and steroid production and hormone production. It also has a
detoxification function.
Protein molecules are synthesized and collected into the cisternal
space/lumen. Smooth ER acts as a storage organelle. It is important in the
production and storage of lipids and steroids that are used in the production
of the new cellular membrane.
2. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
It continues
with the nuclear membrane. Rough ER is called rough because it has ribosomes attached
to its surface. It has a rough membrane and bears ribosome (consisting of
RNA) on its outer surface.
RER is a double-layered membrane system with a network of vesicular space. The interior of the ER
is connected to the perinuclear space of the nucleus through a nuclear
pore and the outer part is connected to the cell membrane. For
movement of molecules mainly transport of mRNA from the nucleus to RER.
ER transportation
system and site of produces secrete and export proteins and few hormones.
Also, check out here structure of mitochondria.
Functions of Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
The key function includes-
1. RER main
function is to help in Protein synthesis.
2. Rough
endoplasmic reticulum processing, modification and folding of the synthesized
proteins and transported out of the cell.
3. Rough endoplasmic
reticulum also helps in synthesizing glycoprotein and phospholipid that is
transferred into the cellular organelle.
4. Smooth
endoplasmic reticulum main function is to synthesize fatty acids (lipid) and
steroids hormones, such as estrogen and testosterone.
5. Smooth endoplasmic
reticulum involves in the detoxification of harmful metabolic byproducts,
inactivates or detoxifies (remove toxic) drug and other potentially harmful
substances, remove the phosphate group from glucose -6- phosphate.
6. Smooth
endoplasmic reticulum storage and release calcium, ions, that trigger
(cause to action), contraction in muscle cells. In muscle cells, the
smooth endoplasmic reticulum is called the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
7. Smooth ER also
plays in the conversion of glycogen to glucose, with glucose -6-
phosphatase present in smooth ER. Enzyme glucose -6- phosphatase,
catalyzing the final step in glucose production in the liver.
8. Glucose -6-
phosphatase enzyme act as a marker for endoplasmic reticulum.








0 Comments