What are Eukaryotic Cells?
Eukaryotic cells have a well-defined nucleus, true nucleus
enclosed within the nuclear membrane or nuclear envelope, membrane-bound
organelles, and rod-shaped chromosomes.
Membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic
reticulum, Golgi complex, and lysosome.
The word “Eukaryote” is derived from Greek words, “eu” means
‘true’ and “karyon” means ‘nucleus’.
Eukaryotes cells may be either unicellular or
multicellular.
Know here what is difference
between prokaryotic
cell and eukaryotic cell?
Types of Eukaryotes
There are four types of eukaryotes cell-
1. Animal Cell
2. Plant Cell
3. Fungal cell
4. Protists, Protozoa
We know that cell is the smallest structural and functional
unit of life.
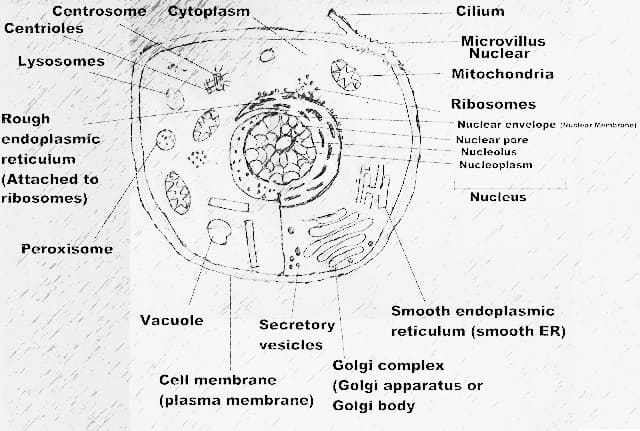
1. Animal Cell
An animal cell is a type of eukaryotic cell that have a true
nucleus and membrane-bound cellular organelles such as mitochondria,
endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi complex, centrioles, microtubules, peroxisomes,
and ribosomes.
An animal cell is a type of eukaryotic cell that doesn’t
have a cell wall.
Check out here difference
between animal cell and plant cell.
2. Plant Cell
Like humans and animals, plants are also made up of cells.
The plant cell is rectangular in shape and comparatively
larger than the animal cell.
A plant cell is a eukaryotic cell, it contains a defined nucleus and has membrane-bound organelles. to perform specific functions. Certain organelles are present in plant cells, and those organelles perform specific functions that are different from animal cells.
The plant cell is enclosed by a cell wall, which is a rigid layer composed of cellulose. The cell wall
provides shape to the plant cell and has rigid structures.

The plant cell membrane is present within the cell wall. It is
the semi-permeable membrane that plays an important role in controlling and
regulating the entry and exit of specific substances within the cell.
Plant cells have a large central vacuole containing
water and dissolved substances.
Plant cells have Plastids, double-membrane organelles
which are found in the cells of plants and algae.
Plastids often contain pigments that are used in photosynthesis,
responsible for manufacturing and storing food, and also have different types
of pigments that can change the color of the cell.
Examples of Plastids include - chloroplasts (chlorophyll,
a green pigment ), chromoplasts, and leucoplasts.
3. Fungal Cells
Like plant cells, Fungal cells have also a rigid cell wall
and organelles including a nucleus.
The cell wall of Fungal cells is made up of chitin and not
cellulose.
Fungal cells do not have chloroplasts, and photosynthetic
pigment chlorophyll is absent.
Some fungi are unicellular such as yeasts, which have tiny
holes in their plasma membrane that allows the cells to exchange
nutrients, cytoplasm, and other organelles from cell to cell.
Fungi can be single-celled or multicellular
organisms. Most fungi are multicellular organisms.
Example of multicellular fungus -
Mold
Example of Unicellular fungi – Yeasts, candida
species
4. Protists
The majority of protists are unicellular eukaryotes, some
are multicellular organisms when compared to plant or animal cells.
Unicellular eukaryotes are single-celled organisms with a
defined nucleus, mitochondria, and other organelle and might
have chloroplasts.
Most protists usually don’t have a cell wall while some
protists might have.
Many protists may have chloroplast containing chlorophyll
pigment while others may have other photosynthetic pigments.
Most Protists have cilia and flagella that help in the
movement of the cells.
Examples of multicellular protists include-
seaweeds, such as multicellular red algae and multicellular green algae, and
Slime mold cells.
Examples of unicellular protists include- unicellular
red algae and unicellular green algae.
Check out here what a prokaryotic cell is? Learn the structure and function of prokaryotic cells.








0 Comments