Intradermal Injection
Intradermal injection is superficial
injection delivers a substance into the dermis,
this skin layer underneath the epidermis (upper skin layer).it is often abbreviated ID.
Intradermal (ID) injection is a technique to deliver or
administer the medication into the dermis layer, which located between the
epidermis and subcutaneous layer o f skin (hypodermis).

Angle of injection for Intradermal injection
The angle of administration for an Intradermal injection is 10-15
degrees.
Check out here angles of
Injections for Intramuscular route, subcutaneous route,
and Intravenous route.
There are mainly 4 type of
parenteral routes of dug administration is used for the administration
of vaccination –
1. Intramuscular route for drug administration
Know here sites
for Intramuscular Injection to administration the medication.
2. Subcutaneous route for drug administration
Check out here common sites
of Subcutaneous Injection.
3. Intravenous route for drug administration, and
4. Intradermal (ID) route of dug administration
Use of Intradermal injection
1. Skin Allergy Tests
Intradermal injection is often used for conducting skin
allergy tests and sensitivity tests.
Examples: Tuberculin
test and Allergy testing
2. Tuberculosis Testing and Testing Antibody Formation
Intradermal injection are most commonly used for diagnostic
purposes such as allergy testing, skin testing, or tuberculosis testing
and testing antibody formation.
The medication injected into dermis layer. Medication is
absorbed slowly because dermis skin layer has a limited blood supply.
The intradermal route of injection has the longest
absorption time for all parenteral routes.
Sites of Intradermal Injection
The most the common injection site for intradermal injection
includes-
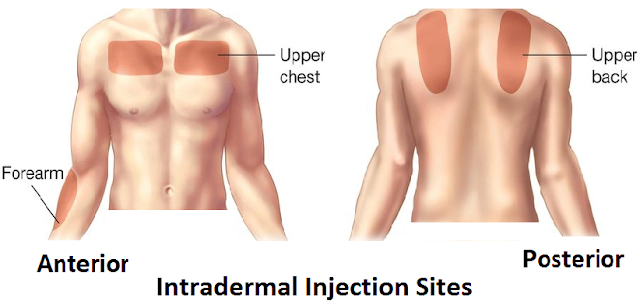
1. Inner surface of the forearm
2. Upper arm
3. Upper chest
4. Upper back, under the shoulder blade (scapula)
Examples of Intradermal Injection;
1. Tuberculin Injection/ Mantoux Test
2. Allergy sensitivity tests
3. Local anesthesia
4. BCG Vaccine
Drug Given Intradermal Route
ID route is used for the Administration of-
1. Tuberculin injection
2. BCG (Bacille Calmette Guerin Vaccine) for tuberculosis
3. Measles vaccine
4. Rabies vaccines
Special Consideration while Administering ID Injection
1. Don’t massage or rub the site after intradermal injection,
it causes aspiration (withdrawing) of
medicine.
2. Needle Bevel should face upwards
Indication of Intradermal Injection
The indication of intradermal injection commonly used for
when-
1. Identify skin allergy to any drugs
2. Intradermal allergy test
3. Tuberculin skin test/ Montoux test
4. Sensitivity test
5. Administration of local Anasthesia prior to an invasive
procedure
Complications of Intradermal Injection
These are the associated complication related to intradermal
injection-
1. Pain at injection site
2. Infection at the injection site
3. Swelling, irritant
4. Larger dose doesn’t administer









0 Comments